Population: Estimate 429,000 (2018)
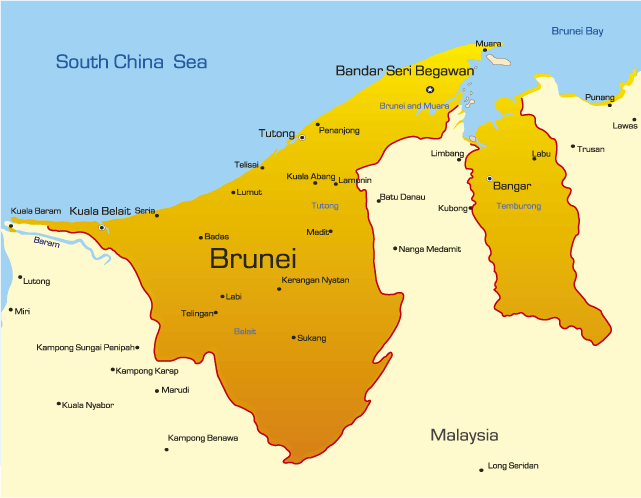
Area: 5 765 km²
Capital City: Bandar Seri Begawan, Population approx. 108.000 (2020)
Brunei’s population was 429,000 in 2018. At the peak of the Bruneian Empire, Sultan Bolkiah (reigned 1485–1528) is alleged to have had control over most regions of Borneo, including modern-day Sarawak and Sabah, as well as the Sulu Archipelago off the northeast tip of Borneo, Seludong (modern-day Manila), and the islands off the northwest tip of Borneo. The maritime state was visited by Spain’s Magellan Expedition in 1521 and fought against Spain in the 1578 Castilian War. During the 19th century, the Bruneian Empire began to decline. The Sultanate ceded Sarawak (Kuching) to James Brooke and installed him as the White Rajah, and it ceded Sabah to the British North Borneo Chartered Company. In 1888, Brunei became a British protectorate and was assigned a British resident as colonial manager in 1906. After the Japanese occupation during World War II, in 1959 a new constitution was written. In 1962, a small armed rebellion against the monarchy was ended with the help of the British. Brunei gained its independence from the United Kingdom on 1 January 1984. Economic growth during the 1990s and 2000s, with the GDP increasing 56% from 1999 to 2008, transformed Brunei into an industrialised country. It has developed wealth from extensive petroleum and natural gas fields. Brunei has the second-highest Human Development Index among the Southeast Asian nations, after Singapore, and is classified as a “developed country”. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Brunei is ranked fifth in the world by gross domestic product per capita at purchasing power parity. The IMF estimated in 2011 that Brunei was one of two countries (the other being Libya) with a public debt at 0% of the national GDP. Forbes also ranks Brunei as the fifth-richest nation out of 182, based on its petroleum and natural gas fields.
Banking
Bank of China has just (April 2016) received permission to open a branch in Brunei. Citibank, which entered in 1972, closed its operations in Brunei in 2014. HSBC, which had entered in 1947, is currently in the process of closing its operations in the country.
Culture

The culture of Brunei is predominantly Malay (reflecting its ethnicity), with heavy influences from Islam, but is seen as much more conservative than Indonesia and Malaysia. Influences to Bruneian culture come from the Malay cultures of the Malay Archipelago. Four periods of cultural influence have occurred, animist, Hindu, Islamic, and Western. Islam had a very strong influence, and was adopted as Brunei’s ideology and philosophy. Brunei’s official main language is Malay but English is also widely spoken as it is a compulsory subject in the majority of the schools. As a Sharia country, the sale and public consumption of alcohol is banned. Non-Muslims are allowed to bring in a limited amount of alcohol from their point of embarkation overseas for their own private consumption.
Geography of Brunei
About 97% of the population lives in the larger western part (Belait, Tutong, and Brunei-Muara), while only about 10,000 people live in the mountainous eastern part (Temburong District). The total population of Brunei is approximately 408,000 as of July 2010, of which around 150,000 live in the capital Bandar Seri Begawan. Other major towns are the port town of Muara, the oil-producing town of Seria and its neighbouring town, Kuala Belait. In Belait District, the Panaga area is home to large numbers of Europeans expatriates, due to Royal Dutch Shell and British Army housing, and several recreational facilities are located there. Most of Brunei is within the Borneo lowland rain forests ecoregion, which covers most of the island. Areas of mountain rain forests inland.
Defense
Brunei maintains three infantry battalions stationed around the country.The Brunei navy has several “Ijtihad”-class patrol boats purchased from a German manufacturer. The United Kingdom also maintains a base in Seria, the centre of the oil industry in Brunei. A Gurkha battalion consisting of 1,500 personnel is stationed there. United Kingdom military personnel are stationed there under a defence agreement signed between the two countries. A Bell 212 operated by the air force crashed in Kuala Belait on 20 July 2012 with the loss of 12 of the 14 crew on board. The cause of the accident has yet to be ascertained. The crash is the worst aviation incident in the history of Brunei. The Army is currently acquiring new equipment, including UAVs and S-70i Black Hawks. Brunei’s Legislative Council proposed an increase of the defence budget for the 2016–17 fiscal year of about five percent to 564 million Brunei dollars ($408 million). This amounts to about ten per cent of the state’s total national yearly expenditure and represents around 2.5 per cent of GDP.
Language Politics and Government Infrastructure
Brunei’s political system is governed by the constitution and the national tradition of the Malay Islamic Monarchy, the concept of Melayu Islam Beraja (MIB). The three components of MIB cover Malay culture, Islamic religion, and the political framework under the monarchy. It has a legal system based on English common law, although Islamic shariah law supersedes this in some cases. Brunei has a parliament but there are no elections; the last election was held in 1962. Under Brunei’s 1959 constitution, His Majesty Paduka Seri Baginda Sultan Haji Hassanal Bolkiah Mu’izzaddin Waddaulah is the head of state with full executive authority. Since 1962, this authority has included emergency powers, which are renewed every two years. Brunei has technically been under martial law since the Brunei Revolt of 1962. Hassanal Bolkiah also serves as the state’s Prime Minister, Finance Minister and Defence Minister. The Royal family retains a venerated status within Brunei.
Infrastructure
The population centres in the country are linked by a network of 2,800 kilometres (1,700 mi) of road. The 135-kilometre (84 mi) highway from Muara Town to Kuala Belait is being upgraded to a dual carriageway. Brunei is accessible by air, sea, and land transport. Brunei International Airport is the main entry point to the country. Royal Brunei Airlines is the national carrier. There is another airfield, the Anduki Airfield, located in Seria. The ferry terminal at Muara services regular connections to Labuan (Malaysia). Speedboats provide passenger and goods transportation to the Temburong district. The main highway running across Brunei is the Tutong-Muara Highway. The country’s road network is well developed. Brunei has one main sea port located at Muara. The airport in Brunei is currently being extensively upgraded. Changi Airport International is the consultant working on this modernisation, which planned cost is currently $150 million. This project is slated to add 14,000 square metres (150,000 sq ft) of new floorspace and includes a new terminal and arrival hall. With the completion of this project, the annual passenger capacity of the airport is expected to double from 1.5 to 3 million. With one private car for every 2.09 persons, Brunei has one of the highest car ownership rates in the world. This has been attributed to the absence of a comprehensive transport system, low import tax, and low unleaded petrol price of B$0.53 per litre. A new 30-kilometre (19 mi) roadway connecting the Muara and Temburong districts of Brunei is slated to be completed in 2019. Fourteen kilometres (9 mi) of this roadway would be crossing the Brunei Bay. The bridge cost is $1.6 billions.
Religion
Islam is the official religion of Brunei, specifically that of the Sunni branch, as dictated by the Madhhab of Shafi‘i. Two-thirds of the population, including the majority of Bruneian Malays adhere to Islam. Other faiths practised are Buddhism (13%, mainly by the Chinese) and Christianity(10%). Freethinkers, mostly Chinese, form about 7% of the population. Although most of them practise some form of religion with elements of Buddhism, Confucianism, and Taoism, they prefer to present themselves as having practised no religion officially, hence labelled as atheists in official censuses. Followers of indigenous religions are about 2% of the population.
Languages
The official language of Brunei is Standard Malay, for which both the Latin alphabet and the Arabic alphabet are used. The local dialect, Melayu Brunei (Brunei Malay), is the most widely spoken language. English is widely used as a business and official language and it is spoken by a majority of the population in Brunei. The Chinese minority in Brunei speak a number of Chinese varieties. Arabic (عربي) is the religious language of Muslims. Therefore, Arabic is taught in schools, particularly religious schools, and also in institutes of higher learning. As of 2004, there are six Arabic schools and one religious teachers’ college in Brunei. A majority of Brunei’s Muslim population has had some form of formal or informal education in the reading, writing and pronunciation of the Arabic language as part of their religious education.
Health
There are four government-run hospitals in Brunei, one for every district. There are also 16 health centres and 10 health clinics.Healthcare in Brunei is charged at B$1 per consultation for citizens and is free for anyone under 12 years old. A health centre run by Brunei Shell Petroleum is located in Panaga. For medical assistance not available in the country, citizens are sent overseas at the government’s expense. In the period of 2011–12, 327 patients were treated in Malaysia and Singapore at the cost to the government of $12 million. Brunei has 2.8 hospital beds per 1000 people.The prevalence of HIV/AIDS is currently at 0.1%, and numerous AIDS awareness campaigns are currently being held. 7.5% of the population are obese, the highest prevalence rate in ASEAN. Also, studies by the Ministry of Health show that at least 20% of schoolchildren in Brunei are either overweight or obese. The largest hospital in Brunei is Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha Hospital (RIPAS) hospital, which had 550 beds in year 1992, is situated in the country’s capital Bandar Seri Begawan. There are two private medical centres, Gleneagles JPMC Sdn Bhd . and Jerudong Park Medical Centre. The Health Promotion Centre opened in November 2008 and serves to educate the public on the importance of having a healthy lifestyle. There is currently no medical school in Brunei, and Bruneians wishing to study to become doctors must attend university overseas. However, the Institute of Medicines had been introduced at the Universiti Brunei Darussalam and a new building has been built for the faculty. The building, including research lab facilities, was completed in 2009. There has been a School of Nursing since 1951.Fifty-eight nurse managers were appointed in RIPAS to improve service and provide better medical care. In December 2008, The nursing college merged with the Institute of Medicines at the Universiti Brunei Darussalam to produce more nurses and midwives. It is now called the PAPRSB (Pengiran Anak Puteri Rashidah Sa’datul Bolkiah) Institute of Health Sciences.
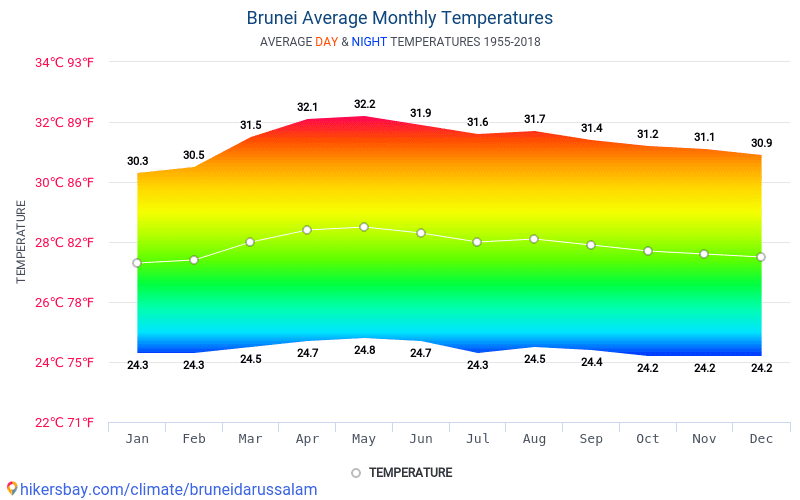
Climate